
Moulding
Moulding is the process of giving shape and size to plastic or rubber material by heating and cooling in a mould.
Mould/Mold
Mould or Mold is a tool which is used to give shape and size of plastic or rubber material and it consist of core ,cavity,ejection system and guiding element etc. The mold is made from metal, usually either steel or aluminium and alloy also used.
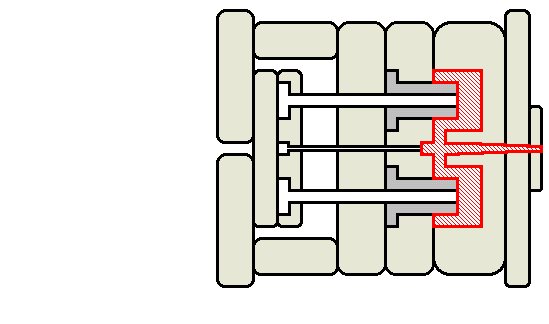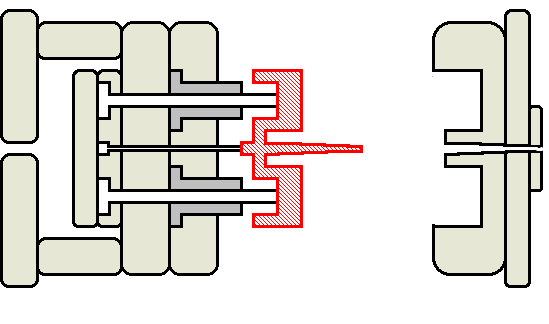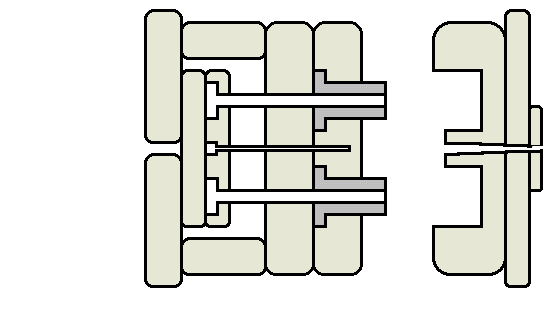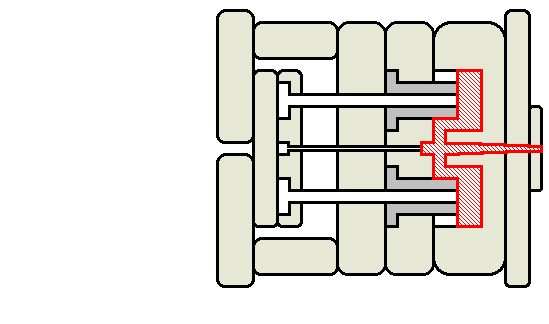
Animated injection mould
Main function of mould
- to give desired shape to the part
- cool and cure the material
- eject the part properly
- to distribute the melt
- to withstand clamping forces and injection pressur
Advantages
• High production rate
• Can process a wide range of materials
• Relatively low labor
• Less or no finishing of parts required
• Scrap material can be recycled and reused
• Low operation cost
• Smooth surfaces
• Full automation is possible with injection molding
• More uniform melting
Disadvantages
• High initial equipment investment
• High startup and running costs
• Difficulty in designing molds
• Contamination of raw material affect the quality of final product
• Requires high pressures
• Problems with required heating/cooling of the plastic material
MOULD MACHINE PARTS

MOULD TOOL PARTS
-
Top Plate
-
Locating or Retainer Ring
-
Cavity Plate
-
Core Plate
-
Core back plate
-
Bottom Plate
-
Spacer
-
Ejector Plate
-
Ejector back plate
-
Feed buttons
-
Guide pillars
-
Sprue bush
-
Sprue puller
-
Guide bush
-
Cavity
-
Core
-
Parting surface

1.TOP PLATE:-
Holds the stationary parts of the mould to the stationary platen of the injection moulding machine.
2.LOCATING RING:-
Fits in to a counter bore in the top plate and is used to locate the mould on the platen of the machine so the nozzle and sprue bushing are aligned.
3.CAVITY RETAINER PLATE:-
Part of the stationary section of the mould in to which the leader or guide pins are mounted. Also used to hold core, cavity blocks,and sprue bushings.
4.CORE RETAINER PLATE :-
Top plate of the movable section of the mould. Forms the parting line of the mould with cavity retainer plate. Used to hold the core blocks.
5.CORE BACK PLATE: -
Mounted behind the retainer plate to keep this plate from bending under the high pressure used in injection moulding.
6.BOTTOM CLAMPING PLATE:-
Holds the moving portion of the mould to the movable platen of the injection moulding machine.
7.SPACER: -
Mounted on the bottom plate under the support plate to form a space to allow the ejector pin move.tom
8.EJECTOR PLATE:-
Counter bored for the heads of ejector pins, ejector return pins, and spur puller pin.
9.Ejector Back Plate:-
Bolted together with the ejector retainer plate to form a unit. Acts as a back up plate for the pins in the ejector retainer plate.
10.FEED BUTTON:-
Pressed into the bottom clamping plate they are land for the ejector plate.
11.GUIDE PILLARS:-
Round bars placed between the support plate and bottom clamping plate used for guiding the linear movement of core and cavity.
12. Sprue bush:-
Butted up against the nozzle of the injection machine. Has a conical-shaped hole through which the material is forced into the mould runner
13. Sprue puller:-
Pin located directly under the opening of the spur. Used to pull the molded spur out of the bushing after shot has been made.
14.GUIDE BUSHES: -
Hardened and ground steel bushing which are pressed into one of the plates serve as bearing surfaces for the leader pins
15.CAVITY:-
The female portion of a mould which gives to the molding its external form.
16.CORE:-
The male portion of a mould which forms the internal shape of the molding.
17.PARTING SURFACES: -
That part of the mould plate adjust to the impression which butt together to form a seal and prevent loss of plastic material.

CHAPTER-I (COMPRESSIOIN MOULD)
INTRODUCTION TO COMPRESSION MOULDS
-
Compression and Transfer Molding Processes are mainly used for
the manufacture of thermosetting plastic products.
-
To some extent this process is also used for thermoplastics components which are otherwise not possible to produce by other conventional processing methods due to processing limitations.
-
Robotics and process automation with microprocessor based control systems have revolutionaries, the entire compression and transfer molding line and specially designed thermo set injection molding process.
-
By proper timing of the knock out system which controls the action of the pins, the cavity is closed before the plunger enters the cavity.
-
The wedges are held along the wear plates by T-slots and keys.
-
Landing buttons or bars are provided for the wedges to make certain that there is no gap between the two halves of the cavity at the parting line when the mould is closed.
-
This type of mould, some times called a basket mould.
CLASIFICATION OF COMPRESSION MOULD
They are classified into three main categories based on automation:-
-
Hand moulds
-
Semi-automatic moulds
-
Automatic moulds
1.Hand Moulds
1.Do not weight more than about 10kg for ease of handling.
2.The material is put into the cavities and the two halves of the mould are assembled and placed between the platens of the press.
3.After the press has been closed and parts molded, the mould is removed from the press closed and the parts molded, the mould is removed from the press and the parts ejected from the mould on a conveniently located bench.
2.Semi-automated moulds
1.These moulds are mounted on to the platens of the press by clamps.
2.The mould is loaded with material and the two halves close. After the pieces have been molded some sort of ejection mechanism pushes the parts out of the cavity or off the plunger.
3.The press operator then places the molded parts in a suitable container or on a bench for flash removal etc. The operator cleans the mould of the excess material and the process is repeated.
3.Automate moulds
1.Do not need and operator once the mould has been set up for production run.
2.The automatic moulds, through the use of combinations of loading devices, timing devices positive ejector systems, sweeps, micro-switches, safety devices and cleaning apparatus, lend themselves well for molding many articles.
3.There is a purpose for each type of mould, and many factors such as the size of the piece part and the production requirements, determine which of the three is used.
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE COMPRESSION MOULDING
Three important factors that must be controlled in compression molding are:
1.Temperature
2.Pressure
3.Cure Time
1.Temperature
-
Temperature for molding thermo-setting materials vary from 270°F to 350°F.
-
Temperatures for molding the various materials can be determined by experimentation or by getting the information from the manufacturer of some particular material.
-
Mould temperatures must be maintained with in ±5°F.
-
For best results molding temperatures not only vary with the material used, but with the geometry of the molded article, the type of mould, and whether loose powder or pre-heated performs are used.
2.Pressure
-
Pressure needed to mould a particular article depends on the flow characteristics of the material, the cavity depth, and the projected are of the piece part.
-
It is recommended that minimum molding pressure of 225kg/cm² of projected area be used.
-
In practice, about 375kg per Cm² of projected area is used to compensate for any variables that may be encountered.
3.Cure Time
-
In compression and transfer molding, cure time is the time elapsed when the movement of the press stops until the pressure on the molded part is released.
-
For smaller and thin wall pieces, cure time may be only a minute or two.
-
On larger pieces, and pieces with thick sections, the cure time may be as high as 15 minutes.
VENTS
-
During the process of compression molding, gases are formed as the chemical reaction takes place in the material.
-
Some provisions must be made to get rid of the gases otherwise poor quality piece parts will be the result.
-
Gas pockets can cause incomplete shots or blistered piece parts.
-
One method of getting rid of the gases is to allow the mould to breathe, that is the mould is closed and then opened again for about 3mm to get rid of the gases and then closed again.
LOADING OF MATERIAL IN COMPRESSION MOULDING
To prevent the wastage of material for efficient molding, it is important to load the proper amount of material into the mould. This is done by one of the following three ways:
-
Volumetric
-
Weight
-
Pre-determined Pre-forms
-
Volumatric
1.The volumetric method is most efficient when used with ferrous materials.
2.A container of pre-determined volume is filled with material and the contents poured into the cavity.
2.Weight
1.The weight method is used with materials in which the amount of material cannot be controlled readily by volume.
2.A pre-determined amount of material is weighed on a balance and then placed into the mould.
PRE-FORMS
1.The third method used is a pre-determined amount of material which has been compressed into a pre-form of desired shape size and weight.
2.The use of pre-forms is a very efficient method of loading moulds.
HAND COMPRESSION MOULD
1.Smaller in size and weight not more than 12kg for Easy Handling.
2.Production is limited to small parts, short runs or Prototype Work.
3.Overall height of the molding is controlled by land areas on mating surfaces of the top force and cavity.
4.Maximum Density of the molding may be maintained by clearance between the side wall of the top force and the cavity.
5.Used as a single cavity mould on a Rotary Press and molding pressure is controlled at each station.
6.Flash must be removed in the land area otherwise it will result in damage or breakage of the lands.
7.It is advisable to provide additional pressure pads outside the cavity.
POSTIVE MOULD (DIRECT &LANDED)
1.Used for high bulk materials and large deep draw parts when maximum density is required.
2.It is single cavity mould and uses and accurately weighed charge of material.
3.All the applied pressure is exerted on the material.
4.Flash between the top & bottom force can be produced in the direction of pressure.
5.Flash thickness varies according to the clearance between the loading chamber and top force.
SEMI-POSITIVE
This type of mould takes the advantages of the free flow of material in a flash mould and the quality of producing dense parts of the positive mould.
SEMI-POSSTIVE VERTICAL FLASH TYPE
1.It controls maximum density and critical dimensions as related to cavity and top force.
2.Easy removal of flash on large parts and leaves no flash line scar on the side of the parts
SEMI-POSSTIVE HORIZONTAL FLASH TYPE
1.It is less costly and more popular.
2.It is recommended for close tolerance parts and assures minimum flash finish.
FLASH MOULD (OPEN FLASH)
Clearance between 0.050mm and 0.125 m is provided so excess material can escape and the cavity is not damaged.
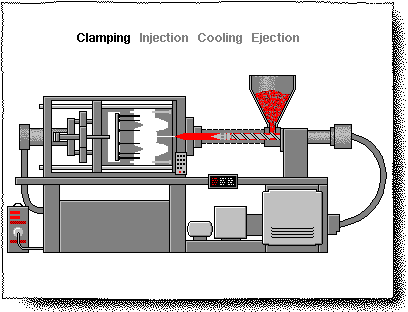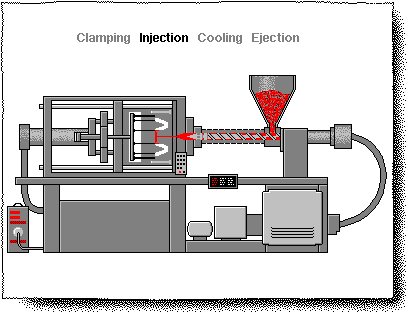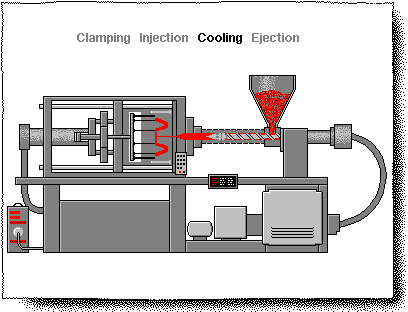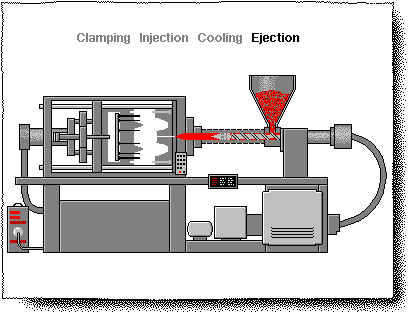
CHAPTER-II (INJECTION MOULD)
Injection Moulding process
"Injection molding”
DEFINITION:
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts from both thermoplastics and thermosetting plastic or other materials. For this purpose injection molding machine is used. Used for manufacturing of variety of parts from small components to entire body panel of cars
• Injection molding process is a manufacturing process used to manufacture parts from plastic, rubber and glasses. • First of all raw material is melted then injected in the mold and product is ready. • Polypropylene is used for table chair and rehl as raw material. • Polypropylene is cheap, has low melting point can be recycled. • In injection molding less material is wasted, and final product is of low cost.
